Precip Accumulation Region of Interest
Notebook Python-AWIPS Tutorial Notebook
Objectives
Access the model data from an EDEX server and limit the data returned by using model specific parameters
Calculate the total precipitation over several model runs
Create a colorized plot for the continental US of the accumulated precipitation data
Calculate and identify area of highest of precipitation
Use higher resolution data to draw region of interest
Table of Contents
1 Imports
The imports below are used throughout the notebook. Note the first import is coming directly from python-awips and allows us to connect to an EDEX server. The subsequent imports are for data manipulation and visualization.
from awips.dataaccess import DataAccessLayer
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from metpy.units import units
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Point, Polygon
2 Initial Setup
2.1 Geographic Filter
By defining a bounding box for the Continental US (CONUS), we’re able to optimize the data request sent to the EDEX server.
conus=[-125, -65, 25, 55]
conus_envelope = Polygon([(conus[0],conus[2]),(conus[0],conus[3]),
(conus[1],conus[3]),(conus[1],conus[2]),
(conus[0],conus[2])])
2.2 EDEX Connection
First we establish a connection to Unidata’s public EDEX server. With that connection made, we can create a new data request object and set the data type to grid, and use the geographic envelope we just created.
DataAccessLayer.changeEDEXHost("edex-cloud.unidata.ucar.edu")
request = DataAccessLayer.newDataRequest("grid", envelope=conus_envelope)
2.3 Refine the Request
Here we specify which model we’re interested in by setting the LocationNames, and the specific data we’re interested in by setting the Levels and Parameters.
request.setLocationNames("GFS1p0")
request.setLevels("0.0SFC")
request.setParameters("TP")
2.4 Get Times
We need to get the available times and cycles for our model data
cycles = DataAccessLayer.getAvailableTimes(request, True)
times = DataAccessLayer.getAvailableTimes(request)
fcstRun = DataAccessLayer.getForecastRun(cycles[-1], times)
3 Function: calculate_accumulated_precip()
Since we’ll want to calculate the accumulated precipitation of our data more than once, it makes sense to create a function that we can call instead of duplicating the logic.
This function cycles through all the grid data responses and adds up all of the rainfall to produce a numpy array with the total ammount of rainfall for the given data request. It also finds the maximum rainfall point in x and y coordinates.
def calculate_accumulated_precip(dataRequest, forecastRun):
for i, tt in enumerate(forecastRun):
response = DataAccessLayer.getGridData(dataRequest, [tt])
grid = response[0]
if i>0:
data += grid.getRawData()
else:
data = grid.getRawData()
data[data <= -9999] = 0
print(data.min(), data.max(), grid.getDataTime().getFcstTime()/3600)
# Convert from mm to inches
result = (data * units.mm).to(units.inch)
ii,jj = np.where(result==result.max())
i=ii[0]
j=jj[0]
return result, i, j
4 Fuction: make_map()
This function creates the basics of the map we’re going to plot our data on. It takes in a bounding box to determine the extent and then adds coastlines for easy frame of reference.
def make_map(bbox, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(20, 14),
subplot_kw=dict(projection=projection))
ax.set_extent(bbox)
ax.coastlines(resolution='50m')
return fig, ax
5 Get the Data!
Access the data from the DataAccessLayer interface using the getGridData function. Use that data to calculate the accumulated rainfall, the maximum rainfall point, and the region of interest bounding box.
## get the grid response from edex
response = DataAccessLayer.getGridData(request, [fcstRun[-1]])
## take the first result to get the location information from
grid = response[0]
## get the location coordinates and create a bounding box for our map
lons, lats = grid.getLatLonCoords()
bbox = [lons.min(), lons.max(), lats.min(), lats.max()]
fcstHr = int(grid.getDataTime().getFcstTime()/3600)
## calculate the total precipitation
tp_inch, i, j = calculate_accumulated_precip(request, fcstRun)
print(tp_inch.min(), tp_inch.max())
## use the max points coordinates to get the max point in lat/lon coords
maxPoint = Point(lons[i][j], lats[i][j])
inc = 3.5
## create a region of interest bounding box
roi_box=[maxPoint.x-inc, maxPoint.x+inc, maxPoint.y-inc, maxPoint.y+inc]
roi_polygon = Polygon([(roi_box[0],roi_box[2]),(roi_box[0],roi_box[3]),
(roi_box[1],roi_box[3]),(roi_box[1],roi_box[2]),(roi_box[0],roi_box[2])])
print(maxPoint)
0.0 10.0625 6.0
0.0 21.75 12.0
0.0 35.1875 18.0
0.0 43.5 24.0
0.0 45.5625 42.0
0.0 47.9375 48.0
0.0 52.0625 54.0
0.0 56.375 60.0
0.0 86.625 66.0
0.0 92.4375 72.0
0.0 94.375 78.0
0.0 95.375 84.0
0.0 98.3125 90.0
0.0 100.125 96.0
0.0 101.6875 102.0
0.0 104.0 108.0
0.0 107.1875 114.0
0.0 115.25 120.0
0.0 129.0 126.0
0.0 136.375 132.0
0.0 141.125 138.0
0.0 145.25 144.0
0.0 147.375 150.0
0.0 5.802169
POINT (-124 42)
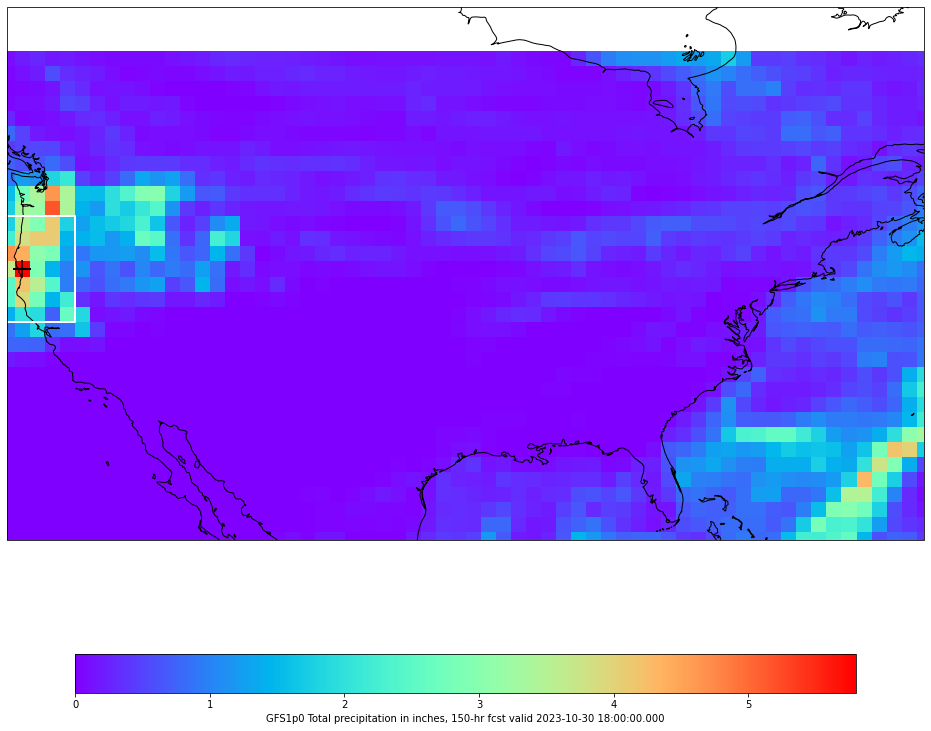
6 Plot the Data!
6.1 Create CONUS Image
Plot our data on our CONUS map.
cmap = plt.get_cmap('rainbow')
fig, ax = make_map(bbox=bbox)
cs = ax.pcolormesh(lons, lats, tp_inch, cmap=cmap)
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs, shrink=0.7, orientation='horizontal')
cbar.set_label(grid.getLocationName() + " Total accumulated precipitation in inches, " \
+ str(fcstHr) + "-hr fcst valid " + str(grid.getDataTime().getRefTime()))
ax.scatter(maxPoint.x, maxPoint.y, s=300,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),marker="+",facecolor='black')
ax.add_geometries([roi_polygon], ccrs.PlateCarree(), facecolor='none', edgecolor='white', linewidth=2)
<cartopy.mpl.feature_artist.FeatureArtist at 0x13eb32340>
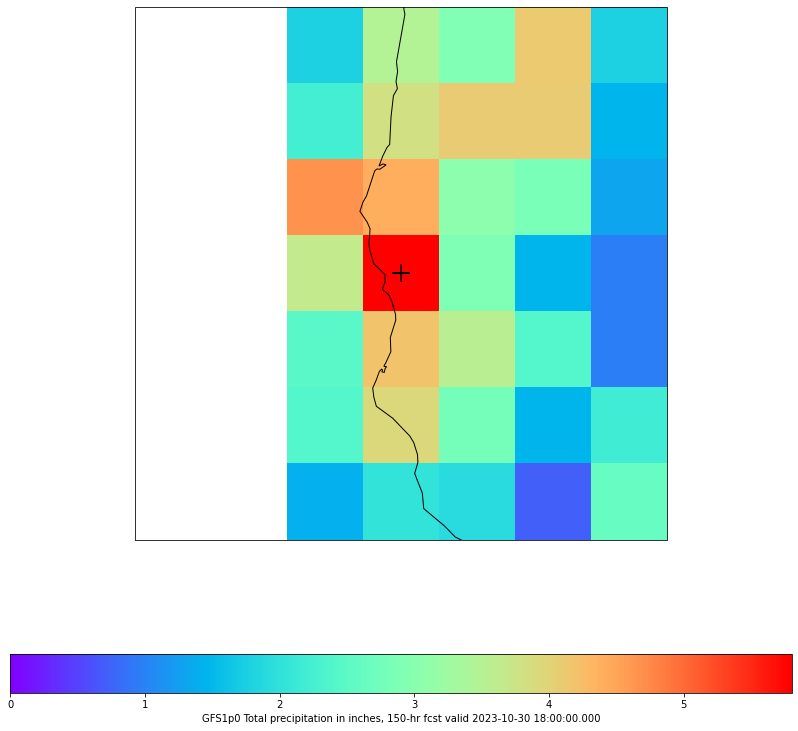
6.2 Create Region of Interest Image
Now crop the data and zoom in on the region of interest (ROI) to create a new plot.
# cmap = plt.get_cmap('rainbow')
fig, ax = make_map(bbox=roi_box)
cs = ax.pcolormesh(lons, lats, tp_inch, cmap=cmap)
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs, shrink=0.7, orientation='horizontal')
cbar.set_label(grid.getLocationName() + " Total accumulated precipitation in inches, " \
+ str(fcstHr) + "-hr fcst valid " + str(grid.getDataTime().getRefTime()))
ax.scatter(maxPoint.x, maxPoint.y, s=300,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),marker="+",facecolor='black')
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x13ed521c0>
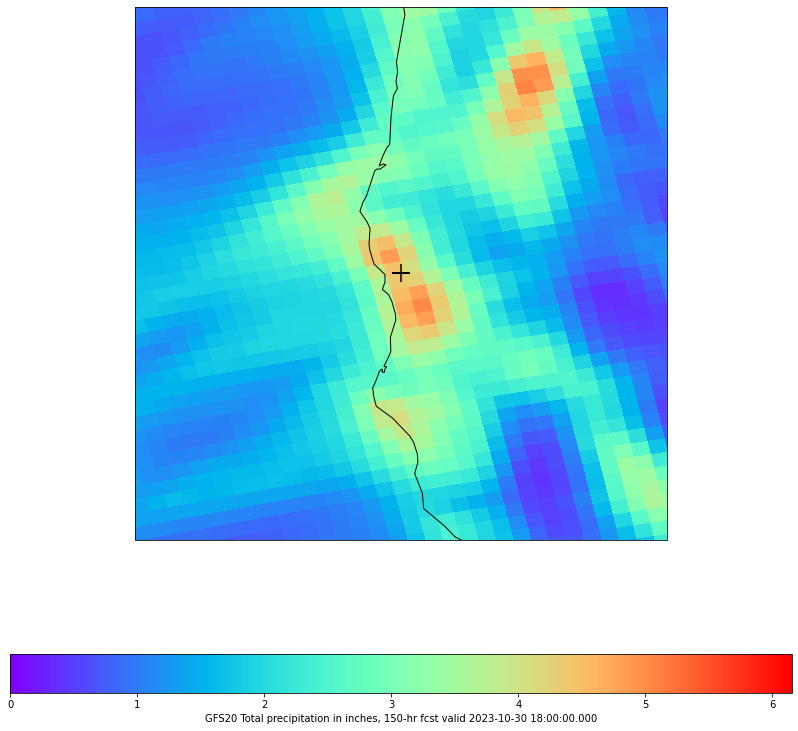
7 High Resolution ROI
7.1 New Data Request
To see the region of interest more clearly, we can redo the process with a higher resolution model (GFS20 vs. GFS1.0).
roiRequest = DataAccessLayer.newDataRequest("grid", envelope=conus_envelope)
roiRequest.setLocationNames("GFS20")
roiRequest.setLevels("0.0SFC")
roiRequest.setParameters("TP")
roiCycles = DataAccessLayer.getAvailableTimes(roiRequest, True)
roiTimes = DataAccessLayer.getAvailableTimes(roiRequest)
roiFcstRun = DataAccessLayer.getForecastRun(roiCycles[-1], roiTimes)
7.2 Calculate Data
roiResponse = DataAccessLayer.getGridData(roiRequest, [roiFcstRun[-1]])
print(roiResponse)
roiGrid = roiResponse[0]
roiLons, roiLats = roiGrid.getLatLonCoords()
roi_data, i, j = calculate_accumulated_precip(roiRequest, roiFcstRun)
roiFcstHr = int(roiGrid.getDataTime().getFcstTime()/3600)
[<awips.dataaccess.PyGridData.PyGridData object at 0x13ecb4eb0>]
0.0 22.5625 3.0
0.0 35.375 6.0
0.0 38.375 9.0
0.0 38.375 12.0
0.0 41.375 15.0
0.0 48.625 18.0
0.0 73.0625 30.0
0.0 94.9375 33.0
0.0 96.125 36.0
0.0 97.0 39.0
0.0 99.375 45.0
0.0 100.0625 48.0
0.0 100.25 51.0
0.0 100.4375 57.0
0.0 100.4375 63.0
0.0 118.25 66.0
0.0 127.625 69.0
0.0 131.125 75.0
0.0 131.375 78.0
0.0 131.5 81.0
0.0 131.875 84.0
0.0 132.875 90.0
0.0 133.375 96.0
0.0 139.1875 102.0
0.0 141.625 120.0
0.0 141.75 126.0
0.0 142.1875 132.0
0.0 143.375 138.0
0.0 148.6875 144.0
0.0 156.25 150.0
7.3 Plot ROI
# cmap = plt.get_cmap('rainbow')
fig, ax = make_map(bbox=roi_box)
cs = ax.pcolormesh(roiLons, roiLats, roi_data, cmap=cmap)
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs, shrink=0.7, orientation='horizontal')
cbar.set_label(roiGrid.getLocationName() + " Total accumulated precipitation in inches, " \
+ str(roiFcstHr) + "-hr fcst valid " + str(roiGrid.getDataTime().getRefTime()))
ax.scatter(maxPoint.x, maxPoint.y, s=300,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),marker="+",facecolor='black')
/Users/scarter/opt/miniconda3/envs/python3-awips/lib/python3.9/site-packages/cartopy/mpl/geoaxes.py:1702: UserWarning: The input coordinates to pcolormesh are interpreted as cell centers, but are not monotonically increasing or decreasing. This may lead to incorrectly calculated cell edges, in which case, please supply explicit cell edges to pcolormesh.
X, Y, C, shading = self._pcolorargs('pcolormesh', *args,
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x13edc39a0>
8 See Also
8.2 Additional Documentation
python-awips:
matplotlib: